07/04/2024 - Articles
Defining project objectives - the key to project success
Let's build the foundation of every successful project: clear, precise and inspiring project objectives. A project objective is not just a vision, but the living blueprint for your success story. Find out why a clear definition is crucial for project success and how to formulate objectives precisely. Delve into different types of objectives, overcome conflicting objectives and use the objective relationship matrix. Discover how clear project objectives not only have a significant impact on alignment, but also on success!
Inhalt:
- Defining project objectives
- Why define project objectives?
- 5 functions of project objectives
- Types of project objectives
- Best practice formulating project objectives
- Tutorial Formulating project objectives: 5 steps
- When to define project objectives?
- Presenting project objectives
- Defining project objectives with software
- Project objectives: The key to project success
What are project objectives?
A project objective is a clear, comprehensive and verifiable description of the target state to be achieved by the project. The project objective usually combines several sub-objectives of different types. All these objectives are clearly defined and elaborated at the beginning of the project and are an integral part of the project plan to guide direction and progress.
DIN 69901-5:2009-1 "Project management - Project management systems - Part 5: Terms" defines the terms "project objective" and "objective definition" under 3.87 and equates them with the English terms "project scope" and "scope definition":
Project objective: totality of individual objectives to be achieved by the project.
Target definition: quantitative and qualitative definition of the project content and the realization conditions to be met, e.g. costs and duration, in target characteristics with usually different target weightings (e.g. mandatory and optional targets).
Why is it smart to define project goals?
The clear definition of project objectives is one of the fundamental tasks in project management. According to a PMO study by Projectgroup 2020, a lack of precise project objectives significantly increases the risk of project failure due to a lack of clear direction and a uniform understanding.
Despite its fundamental importance, many clients and project managers experience difficulties in formulating a clear project objective. Unlike deliverables, deadlines and resources, which can be clearly stated, project objectives represent a desired state - often characterized by vague ideas. The art of formulating objectives lies in expressing these ideas in concrete terms.
A well-formulated project objective is characterized by the fact that its fulfillment can be clearly verified and that all persons involved find themselves reflected in the formulation. A successful objective formulation describes the desired state precisely and concisely in order to minimize the scope for different interpretations.
The definition of project objectives is useful for various reasons
1. Clear Direction
Project objectives provide a clear direction and indicate what the project should achieve. This ensures that all team members and stakeholders are working towards the same result.
2. Define Success Criteria
Defining project objectives enables clear success criteria to be established. These criteria serve as a benchmark to assess whether the objectives have been achieved at the end of the project.
3. Efficient Use of Resources
Clear project objectives facilitate the planning and allocation of resources such as budget, time and personnel. This leads to an efficient use of available resources.
4. Setting Priorities
Project objectives help to prioritize and ensure that all activities are in line with the main objectives and business goals. This helps to avoid distractions and promote project success. A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) helps to determine a project metric per project to determine the extent to which each project in the project portfolio contributes to the company's goals.
5. Motivation and commitment
Clear project objectives provide a clear perspective for team members. Understanding how their work contributes to the overall success of the project increases motivation and commitment.
6. Improve Communication
Project objectives serve as the basis for communication within the team and with stakeholders. Clear project communication supports better understanding and cooperation.
7. Better Project Controlling
With defined objectives, project managers can better control and monitor the progress of the project. This enables timely adjustments to ensure the project stays on track.
8. Promote Learning Processes
Once the project is completed, the defined objectives provide the opportunity to evaluate success, identify learning processes, document lessons learned, extract best practices for future projects and adapt processes accordingly.
In summary, clearly defined project objectives help to ensure that a project is carried out effectively, efficiently and successfully. They create a clear structure and orientation for everyone involved. These principles reflect the SMART method, which provides a clear structure for formulating objectives.
The 5 functions of project objectives
In project management, five functions of objectives can be recognized, viewing objectives not just as endpoints but as living tools that permeate the entire project life cycle.

Control function
Objectives in project management serve as a benchmark for monitoring and controlling progress. By comparing the current status with the defined objectives, deviations can be identified and appropriate measures taken to bring the project back on t
Orientation function
Objectives provide clear direction and orientation for the project team. They define the desired end state and help to communicate common goals. This promotes unity of effort and a shared understanding of the project mission.

Connecting function
Objectives connect different parts of a project. They create a link between the tasks, activities, resources and team members to ensure that all aspects of the project are working in a common direction.
Coordination function
Objectives play a crucial role in coordinating activities in the project. They serve as a reference point for planning and controlling tasks, resources and schedules to ensure that everything is carried out efficiently and effectively.
Selection function
When setting objectives, the project team must make certain choices and decisions. Objectives help in selecting the best ways and means to achieve the project objectives. This includes the strategic selection of resources, methods and approaches.
What types of project objectives are there?
In principle, the number of possible types of objectives that can be relevant for a project is almost unlimited and highly individual. In practice, however, it has proven useful to define a few specific types of objectives.
Project objective / overall objective / main objective / global objective
This is the overarching goal that guides the entire project. It defines what is to be achieved with the project and sets the framework for all activities.
Sub-objectives
These objectives are more specific and relate to certain phases, tasks or milestones within the project. They contribute to the achievement of the overall objectives. Each sub-goal or sub-objective can be further subdivided and specified by further sub-sub-objectives or specific target classes. The most practical target classes are as follows.
Performance objectives
They focus on the effectiveness, efficiency and efficacyof processes or activities. These targets can relate to the quantity of service provided, the use of resources, productivity or other measurable key figures. Performance targets are often quantitative and relate to the quantity or scope of results to be achieved.
Example of a performance target: Increase production capacity by 20% within one year.
Quality objectives
These targets focus on the quality, accuracy or excellence of the results or products. Quality objectives emphasize the fulfillment of certain standards or requirements to ensure that the results achieved meet the desired quality standards. These objectives are often qualitative and concern the characteristics or properties of the results.
Example of a quality objective: Reduce the number of defects in a product by 50%.
Usability objectives / benefit objectives
Objectives that relate to expectations regarding the use of a product, system or service. These objectives describe how users should use the solution in question and what benefits or experiences they expect to gain. Usability objectives are particularly important in the area of product design, software development and the design of services.
Example of an usability objective: Reducing the loading time of a website in order to increase user-friendliness and user interaction.
Deadline targets / time targets
Deadline or time targets are defined time targets for specific milestones or the overall project. They help to define and control the time frame for implementation.
Example of a deadline target: Completion of software development by March 31, 2024.
Cost targets
Targets that relate to the budget and financial resources of the project. They define the financial requirements and restrictions.
Example of a cost target: Limiting the total costs for a construction project to 2 million euros.
Social objectives
Objectives relating to social aspects and relationships. These objectives focus on the well-being of the people involved in or affected by the project and on creating a positive social impact. Social objectives are particularly important to promote a healthy and productive working environment and to strengthen relationships with stakeholders.
Example of a social objective: Introduction of initiatives to promote equal opportunities in the workforce.
Sustainability goals
Goals that relate to environmental or economic sustainability aspects. They may include the integration of environmentally friendly practices or social responsibilities into the project.
Example of a sustainability target: Reduce energy consumption by 20% in the production unit.
Non-objectives / anti-objectives
Non-objectives are exclusion criteria, aspects or conditions that should be deliberately avoided or not achieved. In the context of project management, non-objectives serve to set clear boundaries, specify the objective and avoid misunderstandings. Here are some aspects associated with non-objectives:
Example of a non-objective: not introducing a specific function to limit the scope of the project.
How to formulate project objectives - practical tips
There are different approaches to formulating and defining a project objective. The magic triangle in project management distinguishes between the three target factors of time, cost and performance. In many projects, these factors are essential for the development of objectives by defining cost, performance and deadline targets. Particularly at the start of projects, the objectives can be easily determined and set based on these three parameters.
The project objective therefore comprises the achievement of a desired state (performance objective) by a certain end date (time objective or deadline objective) with a certain use of resources (resource objective or cost objective).
There are also general criteria that should be taken into account when formulating a project objective:
It is very important to involve all stakeholders. This not only provides additional input, but the collaborative development also gives everyone involved a good understanding of the objectives. If these change during the project, the project team can react to these changes.
Furthermore, objectives should be defined as succinctly and concisely as possible and summarized in one or two sentences. A longer formulation can follow in the project description. However, this tends to cause confusion in the context of the objectives. By reducing the objectives to the essentials, they are easy to understand and everyone can see what they are about.
The objectives should be checked regularly, especially for larger or longer projects. They need to be updated in the event of changes. And it is important to check whether they still correspond to your own ideas.
Defining project objectives in 5 steps
In practice, a five-step process for defining objectives has proven successful:
Step 1: Identify objectives
Project objectives are not always clear. A project idea or a customer order alone is often not enough. There are less obvious factors such as unclear client requirements, overarching company objectives, influences from the project environment such as legal regulations and individual stakeholder objectives. It is advisable to proceed as a team and use methods such as the target cross or the Devil’s Quadrangle.
How do you define project goals? Methods and tips
In this article, you will learn how to formulate high-quality project goals using strategic sources such as project ideas, customer requirements and company objectives. It also introduces proven methods such as the SMART method, the magic triangle, the Devil’s Quadrangle and the target cross, which help you to set precise and measurable goals that ensure project success.
Step 2: Precise formulation of objectives
The best approach for defining project objectives is the SMART method. The SMART criteria state that objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time-bound. These objectives can be defined effectively if rough objectives already exist and are now to be planned in more detail. The clear definition according to the SMART formula offers the advantage of facilitating communication within the project team and preventing misunderstandings.
Specific: The objective is described concretely and in detail.
Measurable: The objective can be assessed both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Executable: The objective is appropriate, attractive and motivating for all stakeholders.
Realistic: The objective can be achieved within the specified time with the available resources.
Scheduled: The objectivecan be implemented at a specific point in time.
Using the SMART method, we operationalize the objectives, i.e. we make them measurable in terms of their content, scope and time frame using key figures. Operationalized objectives serve as concrete instructions for action to implement the targets in practice.
Formulate SMART project goals - make success measurable
The SMART method is your key to clearly defining your goals and achieving your dreams! The acronym stands for Specific, Measurable, Attractive, Realistic and Timed - the building blocks for goals that not only sound fantastic, but are actually within reach. Discover how you can take your projects to the next level with SMART and get the motivation in your team crackling
Step 3: Differentiation from non-objectives
Non-objectives are the clear definition of what is NOT to be achieved in the project. They are the opposite of the actual project objectives. The formulation of non-objectives is useful to avoid misunderstandings, to facilitate argumentation in later discussions and to clearly define what will and will not be considered within the project.
Step 4: Prioritizing project objectives
Clear objectives are the key to success in any project. But what happens if there are time constraints or a lack of resources? This is where prioritization comes into play. Clarifying the importance of your objectives helps you to make the right decisions in critical project situations. We differentiate between must-objectives (decisive for the success of the project), should-objectives (influence satisfaction) and can-objectives (additional bonuses). We clearly distinguish these from non-objectives.
MoSCoW method
This procedure for classifying requirements, objectives and tasks according to importance is also known as the MoSCoW method. The acronym MoSCoW stands for:
- Mo - Most important (objective MUST be achieved)
- S - Should (objective SHOULD be achieved)
- Co - Could (objectiveCAN be achieved as an additional bonus)
- W - Won't (non-objectivel)
Prioritize your objectives to increase the success of your project. Try it out and give yourself a clear advantage for your next project!
Step 5: Analyze the objective relationships
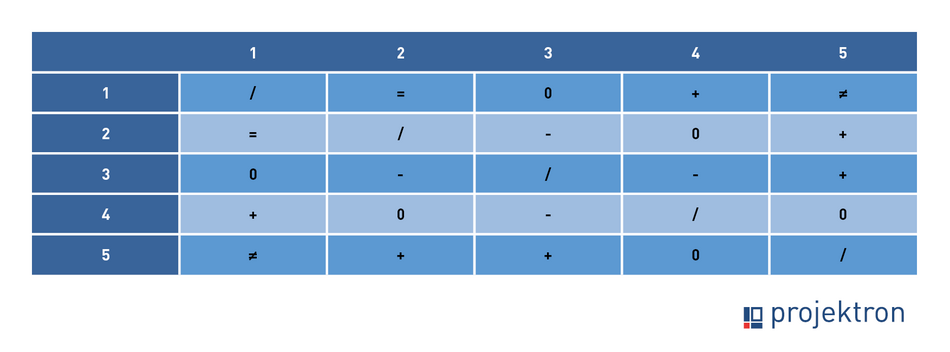
In every project, objectives strive for success, but reality often brings contradictions. From competition to incompatibility, there are five different objective relationships to consider: Identity, Complementarity, Neutrality, Competition and Antinomy. The objective relationship matrix is an effective tool for visualizing and analyzing the different objective relationships in a project. Each objective relationship is represented by a symbol.
- Objective identity (=): These are identical objectives that differ only in their formulation. Solution approach: Both objectives merge into one.
- Objective complementarity (+): Objectives that positively influence each other are complementary. This is the ideal situation for project managers. It is important to use the synergies between the two objectives as an opportunity.
- Objective neutrality (0): Objectives that do not influence each other are neutral. No special measures are required here and both objectives can be implemented.
- Competing objectives (-): Competing objectives that interfere with each other can become a problem. Solution: Negotiate with stakeholders or make a clear prioritization. If you have to pursue competing objectives, include them in your risk management!
- Objective antinomy (≠): Incompatible objectives that need to be corrected behave antinomically. Solution: Do not start the project with such contradictions! Eliminate one of the objectives and deliberately place it "out of scope" or migrate it to another project.
When do the project objectives need to be defined?
The definition of objectives determines the most important characteristic of a project, namely the WHAT: What is the project supposed to achieve? This is why the definition of the project objective or objectives and the scope of the project is at the very beginning of the project planning phase. The HOW, i.e. concrete measures, are only defined later when the objectives are clear.
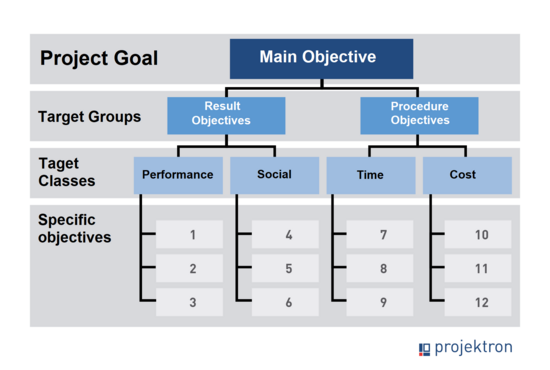
Present project objectives: objective tree or objective hierarchy graphic
The objective tree or objective hierarchy graphic is a visual representation of the hierarchy of objectives within a system or project. This graphic shows the different levels of objectives and their relationships to each other. Typically, hierarchical structures such as in a work breakdown structure are used to show main objectives, sub-objectives and their connections.
With the help of the objective tree, solutions for possible conflicts of objectives with stakeholders can be found in advance. This lays an important foundation for the success of the project, especially if the objectives are unclear, conflicting or difficult to achieve.
Examples of target hierarchies
Example 1 - Overall objective: Increase customer satisfaction
- Sub-objective 1: Improving customer support
- Sub-objective 1.1: Reduce response times
- Sub-objective 1.2: Training of support staff
- Sub-objective2: Increase product quality
- Sub-objective 2.1: Implementation of quality control measures
- Sub-objective 2.2: Use customer feedback for product improvements
Example 2 - Overall objective: Development of a new software application
- Sub-objective 1: Design of the user interface
- Sub-objective 2: Implementation of the backend functionality
- SSub-objective 3: Implementation of user tests
Possible uses of the objective hierarchy graphic
- Order clarification: Clarification of orders with clients, customers and sponsors of the project.
- Teamwork and stakeholder interaction: Clarification or communication of the hierarchy and dependencies of the objectives within the project team and with other stakeholders.
- Identification of deviations: Identification of deviations between the desired target state and reality. This serves as a starting point for a root cause analysis of the deviations.
- Agreement on objectives at management level: Achieving agreement on objectives and objective hierarchy in the management of an organization.
- Personal life goals: Developing personal life objectives and their priorities.
Results and benefits of the objective hierarchy
- Clarity and agreement on objectives: Transparent hierarchy and interrelationships of a system's objectives.
- Risk reduction in the event of conflicting objectives: Early detection and resolution of potential objective conflicts.
- Documented objectives: Structured and documented objectives as a basis for subsequent decisions.
- Forced discussions: The predefined logical structure promotes discussions about main objectives, cause-effect relationships and decision-making processes.
- Graphical representation: Intuitive grasp of objectives at a glance, makes it easier to remember them.
- Achieved transparency: The transparency of the objectives promotes discussions about the hierarchy of objectives.
- Focus on what is important: Team and organization can concentrate on what is really important without getting lost in numerous difficulties and problems.
- Resolution of conflicting objectives: Conflicting objectives can be easily resolved by combining the objective tree and conflict cloud.
Define project objectives with project management software
- Capture and structure project objectives: Users can define detailed project objectives, both overall objectives and sub-objectives. Structuring enables a clear hierarchy and organization of objectives, which improves project planning.
- Capture objectives' details: Users can capture comprehensive information about each project objective, including objective description, operationalized objectives and measurement criteria. This facilitates a precise definition and understanding of project objectives.
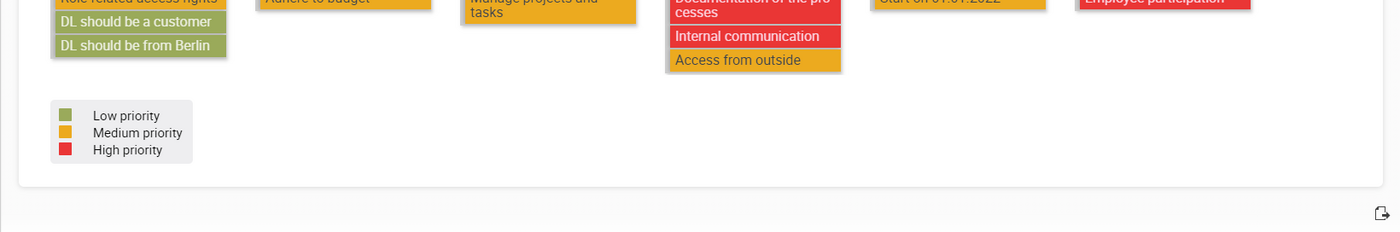
- Categorization and prioritization of objectives: Project objectives can be categorized according to different categories such as cost objectives or deadline objectives. The prioritization with different colors enables a visual differentiation and focus on particularly important objectives.
- Scheduling and monitoring: Users can set a date by which each objective should be achieved. The ability to filter by target date makes it easier to monitor and manage project targets over time.
- Measurability and evaluation of target achievement: The specification of target achievement as a percentage enables a quantitative evaluation of progress. Operationalized objectives and measurement criteria help to objectively measure and evaluate objective achievement.
- Efficient editing of project objectives: Users can edit existing project objectives and add new objectives, allowing flexibility to adapt to changing project requirements. The ability to add multiple sub-objectives at once facilitates the quick definition of detailed objective structures.
- Graphical representation of the objectives structure: The objectives view provides a graphical representation of the objective structure, enabling intuitive visualization and analysis. The colour coding of priorities improves the visual recording and prioritization of project objectives.
Projektron BCS gives you and your team the tools to effectively define, efficiently monitor and multidimensionally analyze your project objectives. You benefit from better planning, execution and evaluation of your projects.
Conclusion: Defining project objectives is essential for project success
The definition of clear project objectives forms the foundation for a successful project process. It creates a uniform focus, enables efficient use of resources and serves as a benchmark for project success. Clear project objectives promote the motivation of the team, facilitate communication and improve the controllability of the project.
The variety of project objectives enables comprehensive control, while methods such as the magic triangle and the objective hierarchy chart help to grasp complex relationships and resolve conflicting objectives. In summary, well-defined project objectives play a key role in ensuring that a project is carried out effectively, efficiently and successfully.

About the author
Like all other departments at Projektron GmbH, the marketing department also attaches great importance to the clear definition and tracking of project objectives. After project completion, the effort is evaluated in detail, learnings are recorded and processes are continuously optimized. Kai Sulkowski is an editor in the marketing department and is always informed about current developments and best practices in project management.
More interesting articles in the Projektron blog

Efficiency vs. effectiveness
What should you do if your project manager demands that you work more efficiently? Work more or deliver better results? We explain the difference using practical examples and provide tips for effective and efficient project work.

Project flowchart
A project flow chart is an important part of the project plan and the basis for many other plans. Here you can find out everything you need to know about the project flow chart, get a template and examples of the project flow chart as a list, network plan and Gantt chart.

Resource planning
Resource planning is a strategically important step in project management. What is a resource plan? What information does it contain? What are the benefits of resource planning in project management? Here's resource planning from A to Z.

Project structure planning
It is considered the plan of plans or the mother of all plans in classic project management: the work breakdown structure (WBS). Find out how you should proceed when creating a work breakdown structure here.
FAQ – Project Objectives
What are project objectives?
Project objectives describe specifically what you want to achieve with a project. They set the direction and serve as a benchmark for success and quality. Clear project objectives help to align all project participants towards a common goal. They also facilitate project management and decision-making during implementation. The more precisely and measurably the project goals are formulated, the easier it is to monitor progress.
What role does goal definition play in effectiveness?
Goal definition is central to the effectiveness of a project because it sets priorities and sharpens focus. Without clear goals, there is a risk that resources will be used ineffectively and inefficiently and that tasks will get out of hand. It also increases the motivation of those involved in the project, as everyone knows what they are working towards. Good goal definition also enables deviations to be identified at an early stage. Overall, it ensures that the project becomes more predictable and easier to manage.
What is the best way to define project goals?
Project goals are best defined using the SMART approach: specific, measurable, attractive, realistic and time-bound. Involve all relevant stakeholders to take different perspectives into account. Also describe the project environment and the expected results so that the goals remain clear to everyone. The more concrete the wording, the easier it is to measure success. Use tools such as goal hierarchies or a goal system to structure main and sub-goals.
What are sub-goals and goal systems?
Sub-goals are intermediate goals that break down larger project goals into smaller, more manageable stages. A goal system structures all project goals hierarchically and shows the relationships between higher-level and lower-level goals. This division into a target hierarchy facilitates planning and control, as progress becomes easier to measure. It also allows you to check specifically whether all relevant aspects have been taken into account. A target system helps you to communicate project targets transparently and track them systematically.
What is the difference between a project target and project scope?
The project goal describes the end result you want to achieve – the project scope defines the work required to achieve this goal. The project scope defines the content, functions and services of the project and distinguishes it from other tasks. A clear distinction helps to prevent ‘scope creep’, i.e. the uncontrolled expansion of the project. Project objectives and project scope therefore always belong together and should be recorded in writing at the start of the project. This ensures that everyone involved knows what is expected and what is not part of the project.
What are social objectives?
Social objectives in project management describe the positive effects that a project should have on the people involved and on society. They ensure that a project is not only economically successful, but also strengthens cooperation, increases employee motivation and creates a positive working atmosphere. This includes, for example, promoting open communication and teamwork, creating equal opportunities and diversity, taking into account the needs of all project participants, and building trust and positive relationships. Social goals contribute to projects being implemented in a sustainable and people-oriented manner.
What are action objectives?
Action objectives (also known as process objectives) describe specific procedures or measures that you want to implement during the project in order to achieve the actual project objectives. They define which actions or work steps are necessary. For example: ‘Create a communication plan within the first week of the project’ or ‘Hold weekly status meetings’. Action goals make projects more manageable because they are easy to measure and check.