10/30/2024 - Articles
PM² Methodology: Structured project management for optimal results
Discover how the PM² methodology from the European Commission can revolutionize your project management. From precise planning to successful implementation, PM² offers a structured and adaptable solution based on proven best practices. The methodology covers the entire project life cycle, is structured and user-friendly, while also offering flexibility for individual requirements.
PM², the project management methodology developed by the European Commission, is a well-thought-out framework for the complex project management requirements involved in implementing EU-funded projects. It is aligned with the requirements of the EU institutions and integrates elements of other methods, PRINCE2, PMI and GPM/IPMA. From organizational to developmental to investment projects, PM² offers a structured approach for all types of projects that not only integrates proven best practices but also offers flexibility for individual adjustments. With PM², you ensure that projects stay on track in both planning and implementation.
Contents:
- What is PM²?
- Project definition and objectives
- The 4 pillars of PM²
- Roles and Responsibilities in PM² Project Management
- The PM² project life cycle
- The PM² Mindsets
- Customizing and tailoring
- PM² Agile
- PM² Code of Ethics and Conduct
- Software for PM² projects
- PM²: Effective project management for optimal results
- Is PM² catching on? An assessment by the author
What is PM²?
PM² (pronounced “P-M squared”) is a project management methodology developed by the European Commission in 2007 and implemented internally in 2008. It is not an isolated method, but combines elements from a variety of globally recognized best practices in project management. This comprehensive and structured approach has been endorsed by many EU institutions as the official project management methodology, which underlines its effectiveness and relevance.
In addition, PM² is actively supported by the “Digital Europe” program, which aims to introduce the PM² methodology and its advantages to a wider audience. Since 2018, it has been available to everyone through the Publications Office of the European Union. In doing so, the European Commission aims to promote the effectiveness of PM² beyond its own interests and to support its use in various organizations.
PM² is a popular framework that is available to all project managers and aims to enable effective management of the entire project life cycle, from project preparation, project planning, project implementation and project control to project completion. The basics of PM², in combination with elements of the S-O-S method, have now been adopted by the PMflex method.
PMflex: flexible project management for public administration
PMflex is a German advancement of the PM² method and offers an innovative, holistic project management system for the public sector that focuses on flexibility and adaptability. In this article, you will learn how PMflex helps to manage projects more efficiently and better address the specific needs of public administration. Discover how PMflex helps you manage projects successfully and future-proof.
PM² provides structured project governance, process guidelines, artifact templates, and guidelines for their use. In addition, it promotes a range of effective ways of thinking to help project teams successfully implement their projects. The PM² methodology is flexible and easily adaptable to the needs of different organizations. The current version of the PM² Methodology Guide 3.1 was published in 2023.

PM² is popular.
Since its publication in November 2016, the PM² Methodology Guide - Open Edition has made it into the top 10 most downloaded publications of the EU bookshop and is often number 1, even leaving the timeless classic “How the European Union works” behind!
Project definition and objectives according to PM²
A project is defined in the PM² as a temporary organizational structure to create a unique product or service within certain time, financial and qualitativerequirements. The main purpose of each project is to achieve measurable improvements for the organization by defining and pursuing clear project goals. The deliverables (project outputs) that are produced during the course of the project serve to achieve project outcomes. These project outcomes (results) serve to generate project benefits in the long term.
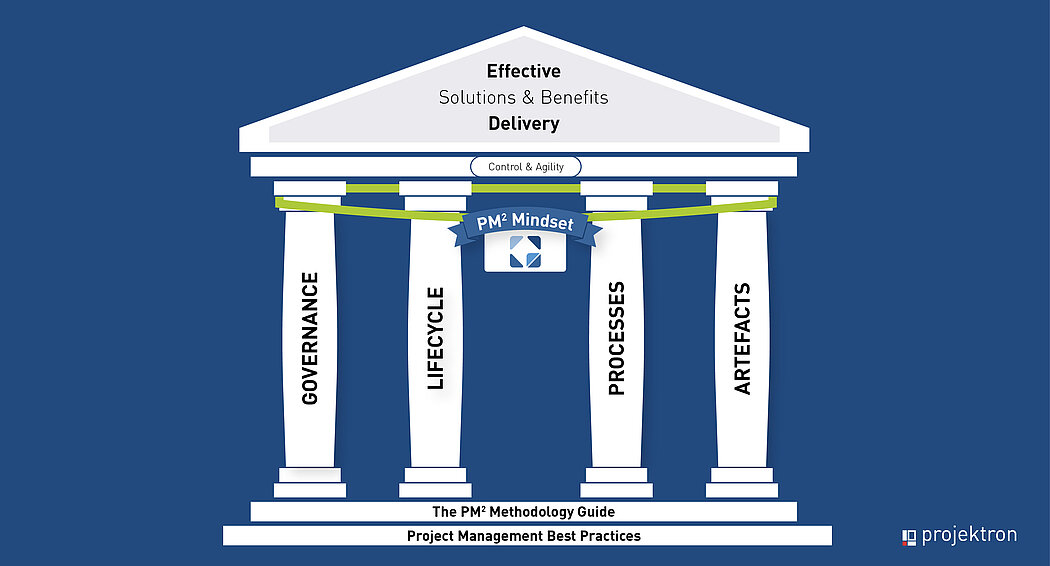
The four pillars of PM²
PM² is based on four essential elements:
- Project governance: This provides the framework for project management decisions. It defines the standard roles in project management and the associated responsibilities, describes the escalation and reporting channels, and ensures that the project meets the desired objectives.
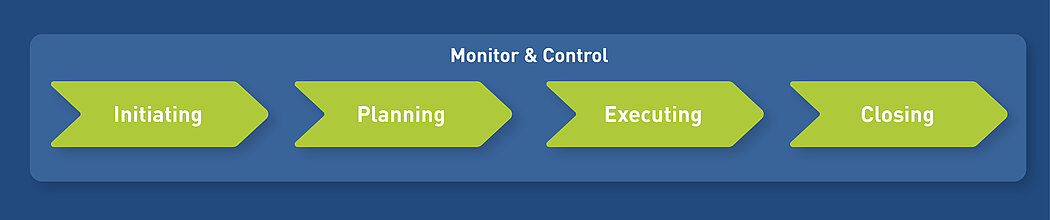
- Project life cycle: PM² takes into account the entire life cycle of a project, from initiation to completion, and provides guidelines for each phase. Four project management phases are defined. The decision to transition from one phase to the next is made at a phase gate and is based on whether the objectives of the current phase have been successfully achieved.
- Processes: PM² encompasses a series of project management processes and activities that are carried out throughout the entire course of the project, often in iterative fashion. These processes are defined in the six PM² management plans as well as in the monitoring and control process group.
- Artifacts: To facilitate the definition, management and communication of projects, the PM² methodology recommends the creation of a series of artifacts. These include a complete set of project templates and detailed guidelines for their use.
In addition, there are the important PM² mindsets: PM² emphasizes certain attitudes and behaviors that enable project teams to focus on the essential aspects of achieving project goals. The mindsets include shared beliefs and values within the project team and help foster a positive attitude and effective collaboration.
Roles and Responsibilities in PM² Project Management
In a PM² project, the roles and responsibilities are divided between the client andcontractor sides.
Client side
- Project Owner (PO – Project Owner): He plays a central role: as the project client, he is largely responsible for defining the business objectives. His task is to ensure that the project results are in line with the defined business objectives, and he bears overall responsibility for the success of the project. Over time, they become the owner of the project results.
- Business Manager (BM – Business Manager): This role plays a supporting role. The Business Manager supports the project owner in their day-to-day business and in defining business goals. They work closely with the project management and coordinate the activities and roles on the customer side.
- Requirements team (BIG – Business Implementation Group): This team provides the requirements manager with technical expertise as needed. It is made up of representatives from the organization and user groups and is responsible for planning and implementing business changes.
Contractor side
- Solution provider (SP – Solution Provider): This party has overall responsibility for the project results and represents the interests of those who create, deliver, and implement the deliverables in the project. In close cooperation with the project owner, he defines and implements the business objectives of the project and appoints the project management.
- Project manager (PM – Project Manager)
- Project core team (PCT – Project Core Team): The team is responsible for creating the project results. The composition and structure of the team are adapted according to the size and type of the project.
Other roles in the PM² project
- Project Support Team (PST – Project Support Team): This team can be implemented as needed to support the core project team with administrative tasks.
- Project Steering Committee (PSC – Project Steering Committee): This committee is responsible for managing the project and monitors it at a high level. It consists of the project owner, the requirements manager, the solution provider and the project management.
- Appropriate Governance Body (AGB – Appropriate Governance Body): This body has a strategic function and is responsible for approving projects, setting project objectives and releasing the required resources.
Roles in a project are distributed across five different levels within the project organization: the executive level (AGB), the steering level (PSC), the management level (PO & SP), the administration level (BM & PM) and the execution level (BIG & PCT). A RASCI accountability matrix or project-specific organizational chart helps project team members understand each person's role in the project and the responsibilities that role entails.
Stakeholders
In addition to the defined roles and responsibilities, it is crucial for the success of the project to effectively identify all relevant stakeholders and manage their engagement. Stakeholders are individuals or groups that affect or are affected by the activities, services or results of a project. PM²'s stakeholder management is very similar to that of GPM/IPMA.
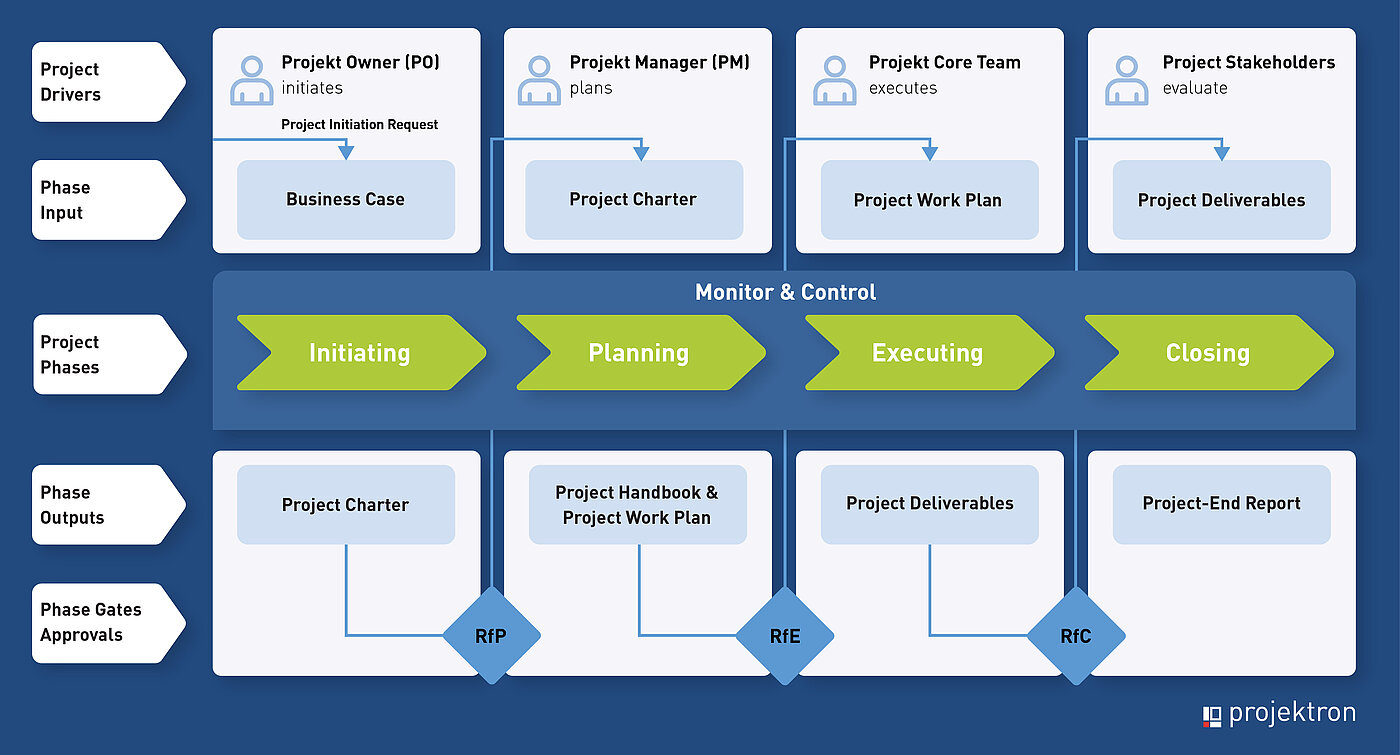
The PM² project life cycle
If these goals are achieved, the transition to the next phase can take place. The phase transitions are checkpoints at which planning maturity, implementation maturity and, finally, maturity for completion must be demonstrated. Each phase has various key artifacts and a specific owner or assigned role.
PM²-Project Phase 1: Initiating
The Initiating Phase marks the start of every PM² project and lays the foundation for successful planning and execution. Its primary goal is to clearly and concisely define the project objectives and constraints, ensuring that they are always aligned with the organization's strategic objectives.
- Central to this phase is the initiation meeting, which brings together project initiators and owners to discuss relevant project information and determine the next steps. The result is a better understanding of the project context.
- The project initiation request, created by the requirements manager, forms the foundation of the project. It includes cost and effort estimates, the time frame for completion, internal or external impacts, the relevance of the project, success criteria, and risks.
- The requirements manager then develops the business case. This document explains the reasons for the project and contains a description of the business context, a problem and project description, the business justification, and an analysis of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. In addition, detailed cost and time schedules are presented.
- The project charter, written by the project management team, forms the basis for detailed project planning. It defines the project objectives in terms of content, time, finances and quality, as well as general requirements, risks and constraints. In addition, project milestones and deliverables are clearly stated to ensure a clear focus for the project.
The business case and project charter are submitted to the project steering committee or an appropriate decision-making body. This body is authorized to decide whether or not to accept the project charter.
To complete the initiation phase and move on to the planning phase, the activities and artifacts of the initiation phase must be reviewed and approved. This is to prepare the project planning and ensure that the project has achieved the necessary planning maturity (RfP – Ready for Planning).
PM² Project Phase 2: Planning
During the planning phase, a concrete implementation plan is developed from the defined project goals. Here are the steps that are carried out in this phase:
- The planning kick-off meeting marks the start of the planning phase and aims to ensure that all project participants are clear about the project scope and the expectations of key stakeholders. During this meeting, project plans are discussed and initial project risks are identified. The project management presents the main elements of the project mandate and schedule and raises awareness of key project roles, risks, constraints and assumptions.
- The project manual, created by the project management in collaboration with the requirements manager, is one of the most important deliverables of this phase. Together with the project work plan, it forms the basis for managing and executing the project and documents objectives, dependencies, constraints and assumptions, the selected project management approach, critical success factors, roles and responsibilities, project processes and guidelines, and adaptations to the underlying project management methodology.
- The project stakeholder matrix, also created by the project lead and the requirements manager, identifies all relevant stakeholders, provides their contact details and defines their roles in the project.
- The project work plan substantiates the project scope and defines the specific work packages and associated deliverables, structuring them. Its components include the work breakdown structure, detailed effort and cost estimates, and a schedule.
The planning phase ends with the review and approval of the phase activities and artifacts by the project steering committee, which means that the project has reached the so-called ready for execution (RfE) stage and can enter the next phase.
PM² project phase 3: execution phase (executing)
During the execution phase, the goals defined in the project work plan are put into practice. The project team carries out planned activities and works continuously to achieve the defined goals.
- The kick-off meeting of the execution phase (Execution Kickoff Meeting) ensures that the entire project team is familiar with the central components and rules of the project. The business case, the project charter, the project manual, the project work plan and all other relevant project plans and protocols are discussed and minutes are taken.
- Project coordination is crucial to provide ongoing support to the core project team. The project management ensures that resources are assigned to the appropriate activities, regular quality checks are carried out, and communication with project team members is maintained.
- Quality assurance is the responsibility of the project management and aims to ensure that project work meets established quality standards, methodologies, and best practices.
- Project reporting is an important part of the implementation phase to continuously communicate project progress and performance to stakeholders and controlling. This includes the project status report, the project progress report, the quality review log, the contractor status report and other user-defined or ad hoc reports.
- Information distribution is carried out in accordance with the communication management plan to keep stakeholders regularly informed and involved.
To complete the implementation phase, the required activities and artifacts are first reviewed and approved by the project management before being finally approved by the project steering committee. This makes the project ready for closing (RfC).
PM² Project Phase 4: Closing
The final phase, as the last stage of a project, is dedicated to the final execution of all project activities and the documentation of the project's final state. The finished results are officially handed over to the project owner. The following steps are carried out in this phase:
- At the project close-out meeting (Project-End Review Meeting), the project management invites the project core team to reflect on the project experiences, evaluate the project performance, discuss lessons learned and best practices, and develop recommendations for future projects. Identifying lessons learned and developing recommendations after the project has ended helps to learn from the project experiences and improve the way future projects operate.
- The project close-down report is prepared by the project management after the project close-down meeting. This report documents best practices, challenges, solutions to problems encountered and serves as a knowledge base for future projects.
- The administrative close-down takes place after the project close-down report has been completed. The project management ensures that all deliverables have been accepted by the stakeholders and that all documentation has been checked, organized and archived. The project team is officially dissolved and the resources released.
The project's success is officially recognized as soon as the final phase is completed and the project owner has approved the project. The administrative closure marks the transition from “project mode” to “operating mode”.
Project monitoring and project controlling in PM² (Monitor & Control)
During monitoring and control, all work is observed from the project manager's point of view. Monitoring involves measuring ongoing project activities and monitoring project variables (costs, time, effort) based on project plans. Controlling involves identifying corrective action to eliminate deviations from plans and to address problems and risks appropriately.
The PM² Mindsets
The processes, artifacts, tools and techniques of the PM² methodology help project managers to make decisions about trade-offs between the project dimensions of time, cost, scope and quality. The PM² mentality consists of attitudes and behaviors that help project team members to focus on what is really important to achieve project goals. Together, they help to manage the complexity of project management in organizations and make the PM² methodology both more effective and more complete.
Project managers and project staff who practice PM²:
- apply PM² best practices to the management of their projects.
- keep in mind that the methodology is there to serve the projects and not the other way around.
- Strive to deliver project results with maximum value rather than just following plans.
- Promote a project culture of collaboration, clear communication and accountability.
- Ensure the support and involvement of the project sponsor and stakeholders throughout the project, including in the planning and implementation of organizational changes needed to achieve targeted project benefits.
- Invest in developing their technical and behavioral skills to become better project managers.
- Share knowledge, actively deal with the experience gained and contribute to improving project management within their organization.
- are inspired by the PM² guidelines for ethics and professional behavior. These guidelines are detailed on two pages in Appendix G of the PM² Project Management Methodology Guide Open Edition.
PM² mindsets are the glue that holds the PM² processes and practices together, providing all PM² practitioners with a common set of beliefs and values.
Customizing and Tailoring
To ensure that the methodology meets the requirements of the project, a certain amount of customizing or tailoring may be required.
Tailoring involves making changes to specific parts of the methodology (e.g. process steps). This is done to adapt the methodology to the needs of specific project types (e.g. IT, events, etc.), taking into account organizational processes, guidelines and culture. Tailoring is more useful at the organizational level, but minor adjustments can also be made at the project level. All adjustments should be documented in the project manual.
However, since every project is unique, additional customization may also be required. This is done at the project level and reflects the specific management requirements of the project.
The following guidelines must be considered for all adjustments:
- Significant deviations from the methodology should be avoided.
- There should be a balance between the control needs of a project and the additional effort that this control requires.
- The tailored and customized approach should be in line with the spirit of the PM² methodology, as reflected in the processes, templates, guidelines and mindset.
PM² Agile
The application of PM² may require adjustments to the specific needs of a project. Given the complexity of many projects, an adaptive, hybrid, and agile approach may be necessary to respond flexibly to changes and achieve project goals.
Agile methods can be seamlessly integrated into PM².
PM² Agile and PMflex Agile: Agile project management for the public sector
In the public sector, agile project management methods are becoming increasingly important. PM² Agile and PMflex Agile each offer customized approaches to making projects more efficient and flexible. PM² Agile combines proven methods of the European Commission with agile practices, while PMflex Agile offers a specially developed, holistic solution for public administration. In our article, we compare these two approaches and show which one is best suited to your specific requirements.
PM² Code of Ethics and Conduct
The PM² Code of Ethics and Conduct and personal and professional virtues are fundamental to the work of PM² practitioners. They promote ethical behavior, professional development and a positive work environment. They are also defined as part of the PM² methodology and set out in the official guide.
The Code of Conduct focuses on moral principles and professional behavior. The most important principles are:
- Independence: Decisions should serve the public good, not private or other interests.
- Impartiality: All decisions should be made impartially.
- Objectivity: Conclusions should be balanced and based on thorough analysis.
- Loyalty: Loyalty to the organization is essential to its independence and objectives.
The virtues refer to a person's personal strengths and are the means between extremes. Some of the important virtues are:
- Wisdom: The ability to set appropriate goals and understand the meaning of our actions.
- Judgment: The ability to evaluate right from wrong and determine the perception of things around us.
- Insight: The ability to perceive, analyze, and understand things correctly.
- Courage: The ability to take risks in pursuit of right goals.
- Honesty: The ability to tell the truth about ourselves and be transparent.
- Other virtues include justice, generosity, kindness, humor, calmness and temperance.
The application of these virtues leads to effective and efficient performance and makes it possible to achieve personal and professional goals. They are crucial for developing professional skills and should be applied transversally.
Projektron BCS – ideal for PM² projects
Projektron BCS offers excellent support for the PM² methodology, which was developed specifically for projects within the European Union and its institutions. The software enables efficient structuring of the phases, roles and artefacts required for PM². The flexibility of Projektron BCS in stakeholder management and reporting is particularly noteworthy. With its configurable functions, the software seamlessly adapts to the requirements of the PM² methodology, ensuring precise and targeted implementation of your EU projects or other projects in the public sector.
In addition, Projektron BCS impresses with its comprehensive customization options, which make it possible to flexibly integrate special requirements of PM² projects. The software supports structuring and documentation in accordance with the specific PM² requirements, thereby offering you a powerful tool for successfully implementing your projects.
See the advantages of Projektron BCS for yourself and test the software free of charge. Start your test today and see how Projektron BCS can optimize your project management processes.
PM²: Effective project management for optimal results
The PM² methodology offers a comprehensive and structured approach that covers the entire project life cycle. Its four pillars – project governance, project life cycle, processes and artifacts – ensure that projects are not only planned and monitored systematically, but can also react flexibly to changes. The methodology promotes clear communication, defines precise roles and responsibilities, and creates a solid basis for the successful implementation and completion of projects.
However, it is important to consider the possible limitations of PM². While the methodology offers a high degree of flexibility and adaptability in many areas, its complexity and the volume of necessary documentation can be a challenge, especially for smaller projects or organizations. In addition, the need for adaptation and customization can increase the implementation effort. Despite these criticisms, PM² remains a valuable tool for comprehensive and effective project management that enables organizations to successfully complete projects and continuously improve their project management.
Is PM² catching on? A critical assessment by the author

About the author
Kai Sulkowski is an editor in the marketing department of Projektron GmbH and is deeply involved with current trends and developments in project management. Through his research and engagement with PM² and PM² Agile, he has developed a thorough understanding of the method, which enables him to communicate complex concepts in a practical and understandable way.
PM2 is a pragmatic and easily accessible project management method that can be quickly grasped, even by those with no prior knowledge. It offers a clear structure through a defined role model and unambiguous responsibilities, which is particularly advantageous for organizations that depend on structured processes. Another plus is the flexible adaptability (tailoring). The templates provided for important project artifacts also help to minimize the effort required to set up a project and ensure consistent documentation.
PM2 is well suited for the public sector, which is often structured in a highly hierarchical way: the governance model and the clear definition of roles and responsibilities provide the necessary structure that these organizations are familiar with. The standardization of processes and the importance of documentation in PM2 help to ensure that projects run in a traceable and documented manner – an important advantage in the public sector, where reports and reference documents often remain relevant even after the project has
However, the guide also has serious gaps. For example, it lacks advice on how to deal with typical project hurdles or possible termination criteria. The guide also remains too vague in crucial areas, such as the analysis of the project environment. Since PM2 is positioning itself for EU authorities and their projects, a more detailed explanation of how to take into account EU-specific organizational structures would have increased the benefit.
Despite these limitations, PM2 could become more established in Europe. In particular, the low barriers to entry and certification costs, as well as the lack of prerequisites for most certificates (Basic, Essentials, Advanced), make the method attractive. In Germany, its dissemination could be limited by the already well-established methods such as IPMA, PMI and V-Modell XT. However, PM2 offers a lightweight and flexible alternative for organizations that prefer a leaner method but still want to rely on an EU-compatible standard.
More interesting articles on the Projektron blog

Project management software comparison
Get an up-to-date overview: We compare 15 of the most popular and best project management software solutions. Start here, discover the market and compare for yourself!

PRINCE2 in project management
PRINCE2 is a process-oriented PM method, can be scaled and places the benefits of a project at the center of project management. Our specialist article provides an introduction to the basic idea, strengths and weaknesses of the PRINCE2 method.

Scrum in software development
When it comes to agile software development methods, there is one term you cannot avoid: Scrum. But what exactly is Scrum and how does it develop its strengths in software development?

Hybrid PM
Classic or agile? If the decision between these two approaches is difficult, a combination of two or more project management methods is probably the right way to go. Find out everything you need to know about hybrid project management in this article.