03/11/2025 - Articles
PRINCE2 project management method: principles, strengths and weaknesses
As standardized approaches, project management methods provide guidance for the planning, execution and controlling of projects. PRINCE2 is a process-oriented method that can be scaled and puts the benefits of a project at the center of project management. Our technical article offers an introduction to the basic idea, strengths and weaknesses of the PRINCE2 method.
Contents
- What is PRINCE2?
- What does the PRINCE2 method involve?
- The 7 fundamental principles of the PRINCE2 method
- The 7 practices of the PRINCE2 method
- The 7-phase process of the PRINCE2 method
- What roles and responsibilities are there in PRINCE2?
- What's new in PRINCE2 7?
- PRINCE2 Agile: Is the PRINCE2 method agile?
- Promoted strengths and advantages of the PRINCE2 method
- Assumed weaknesses and disadvantages of the PRINCE2 method
- Integration of PRINCE2 with other methods and frameworks
- Applying the PRINCE2 method: certifications and training
- Which project management software is suitable for the PRINCE2 method?
- Best Practice: PRINCE2 implementation at DVZ M-V with Projektron BCS
- Conclusion: Why PRINCE2 remains relevant for companies
What is PRINCE2?
With over a million certificates issued and a presence in more than 150 countries, PRINCE2 is one of the world's leading project management standards. It is considered the most important project management standard in Great Britain.
At its core, PRINCE2 is more than just a method: it is a comprehensive project management system that provides a complete control model for projects of all types and sizes. Unlike other approaches (e.g. PMI or IPMA), PRINCE2 does not so much describe the operational implementation of individual tasks as it focuses on the overarching structure and control of projects.
PRINCE2 consists of:
clearly defined processes for managing the entire course of the project
specific roles and responsibilities,
standardized management templates (e.g. business case, risk register),
established methods for results orientation and project control.

PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments)
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a process-oriented project management framework used worldwide for the structured and controlled execution of projects.
PRINCE2 is more than just a method: a systematic approach to project success
A key feature of PRINCE2 is its product-based approach: the focus is on the deliverables (products), not just on activities. In addition, PRINCE2 requires continuous business justification – projects should always make economic sense and provide real benefits.
Thanks to its modular structure, PRINCE2 can be applied across industries and flexibly adapted to the needs of organizations and projects of any size. PRINCE2 thus offers an internationally proven best-practice approach for the successful planning, management and completion of projects.
A brief overview of the history and development of PRINCE2
PRINCE2 was developed from the original PRINCE methodology, which was published by the British government in 1989. This first version was an adaptation of the existing PROMPT (Project Resource Organization Management Planning Techniques) method, which was developed in the 1970s. PRINCE was originally designed for IT projects and was difficult to apply in other areas due to its strict rules.
To make the framework more universally applicable, PRINCE2 was published in 1996 by the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA), a British government agency. This new version was developed to be suitable for projects of all types and sizes. Since then, PRINCE2 has been continuously developed and updated several times to meet current requirements and reflect best practices in project management. PRINCE2 7 was published in 2023. The retention of the name “PRINCE2” (instead of “PRINCE3”) is intended to express that the method remains true to the basic principles.
In 2000, the CCTA was integrated into the Office of Government Commerce (OGC), which was later administered by the Cabinet Office. In 2013, the management and further development of PRINCE2 was transferred to AXELOS, a joint venture between the UK government and Capita. Since 2021, responsibility for PRINCE2 has been with PeopleCert, a leading global certification provider that continues to develop the methodology and integrates international standards.
Who works with PRINCE2?
PRINCE2 has established itself worldwide as one of the leading project management methods. It is used in over 150 countries and is available in several languages. PRINCE2 is particularly widespread in Europe, especially in the United Kingdom, Germany, the Netherlands and Scandinavia. However, it is also increasingly used in Australia, Asia and North America.
PRINCE2 is used in a variety of industries, including:
| Publuc sector: Many government agencies around the world use PRINCE2 to plan and implement public projects | |
| IT and Software development: Companies use PRINCE2 to manage complex IT projects, often in combination with agile methods. | |
| Construction and engineering: PRINCE2 helps to manage large construction projects in a structured way and to minimize risks. | |
| Finance and insurance: banks and insurance companies use PRINCE2 to comply with regulatory requirements and improve their processes. | |
| Healthcare: hospitals and pharmaceutical companies use PRINCE2 to efficiently manage research and digitization projects. |
The universal applicability of PRINCE2 makes it attractive for companies and organizations of all sizes – for public institutions and administrations, from small start-ups to multinational corporations.

Jannik Knoblich, Project Manager, Modernization & Digitization, E-Government, Hanseatic and University City of Rostock, Office for Digitization and IT
“The project management of the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock is based, among other things, on the cornerstones of the project management methodology PRINCE2. Accordingly, the use of the BCS is aligned with the methods. Functions that can be used by the module ‘PRINCE2’ implemented in the BCS are helpful here.”
What advantages does PRINCE2 offer over other methods (e.g. PMBOK, Agile)?
PRINCE2 offers some key advantages over other project management methods:
| Structured and scalable approach: WhilePMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) is a knowledge framework, PRINCE2 offers a concrete methodology with clearly defined processes and roles. This often makes it easier to apply in practice. | |
| Process orientation: PRINCE2 places a strong focus on clear process steps and decision-making mechanisms, which makes it particularly attractive for organizations with complex structures. | |
| Flexibility and adaptability: Although PRINCE2 provides a clear structure, it can be adapted to the specific needs of a company or project. This distinguishes it from more rigid methods. | |
| Focus on the business case: PRINCE2 ensures that every project has an economic justification and is continuously evaluated, leading to better long-term investment decisions. | |
| Integrated risk management: Unlike many agile methods, which focus heavily on iterative development, PRINCE2 takes comprehensive risk management into account from the outset. | |
| Compatibility with agile methods: PRINCE2 can be combined with agile frameworks such asScrum or Kanban. The specially developed extension PRINCE2 Agile enables companies to combine the structure of PRINCE2 with the flexibility of agile methods. | |
| International recognition: PRINCE2 certifications are recognized worldwide and are valued by many companies as proof of a project manager's qualifications. |
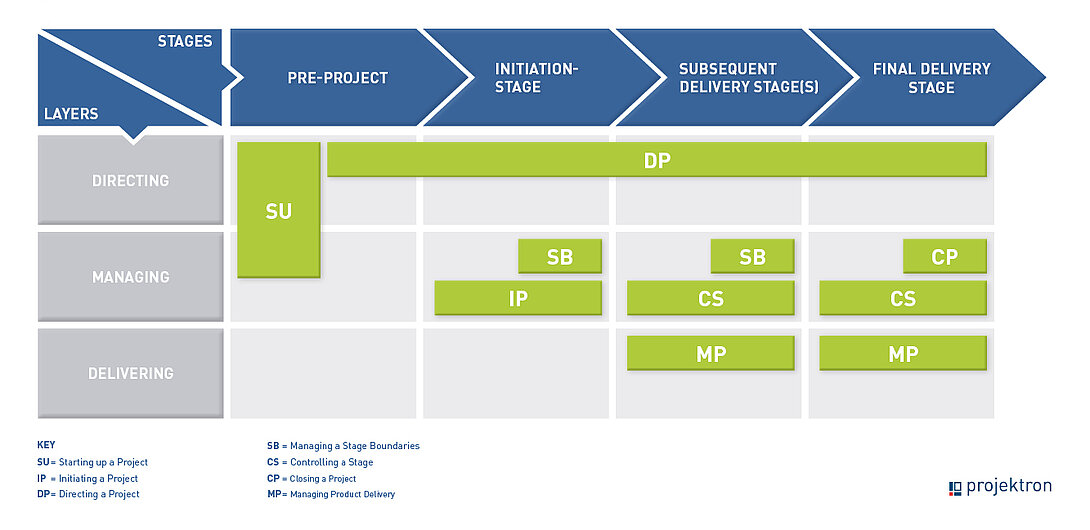
What does the PRINCE2 method consist of?
The method is based on a clearly structured framework that is divided into seven basic principles, seven core practices and seven processes. This interplay ensures that projects can be systematically planned, managed and completed from start to finish. The seven fundamental principles define the basic rules that must apply in every PRINCE2 project, while the seven core practices cover the central aspects of project management, such as the business case, organization and risk.
7 basic principles | 7 practices | 7 processes |
|---|---|---|
| ◆ Continuous business justification | ✏️ Business case | ⚙️ SU: Starting up a project |
| ◆ Learning from experience | ✏️ Organization | ⚙️ IP: Initiating a project |
| ◆ Defined roles and responsibilities | ✏️ Quality | ⚙️ DP: Directing a project |
| ◆ Managing via management phases | ✏️ Plans | ⚙️ CS: Controlling a stage |
| ◆ Managing according to the exception principle | ✏️ Risks | ⚙️ SB: Managing a stage boundary |
| ◆ Product orientation | ✏️ Changes | ⚙️ MP: Managing product delivery |
| ◆ Adapting to the project environment | ✏️ Progress | ⚙️ CP: Closing a project |

The basic idea of PRINCE2
The basic idea of PRINCE2 is that a project has a business justification at all times. This ensures that a project is only continued or completed if it yields a benefit.
The 7 basic principles of the PRINCE2 method
The seven principles of PRINCE2 form the backbone of the entire framework. They create a reliable framework that enables project teams to work in a clearly focused, targeted and controlled manner. Each principle helps to
minimize risks
clearly allocate responsibilities
ensure project success
Principle 1: Continuous business justification
This principle states that a project should only be started and continued if it yields a clearly defined economic benefit. A valid business case must be created at the beginning and continuously reviewed throughout the entire course of the project. This prevents resources from being allocated to projects whose benefits dwindle over time or when market conditions change.
Practical example
A medium-sized company plans to implement a new IT platform to optimize processes. The business case created documents ROI and savings, which are regularly reviewed during the project. If market conditions change drastically, the project is adjusted or canceled to ensure resources are used wisely.
Principle 2: Defined roles, responsibilities, and relationships
Clear roles and responsibilities ensure that everyone knows what they have to do and who makes the decisions. This helps to avoid misunderstandings and enables quick reactions.
Practical example
When a new transportation network is being built, the project manager is responsible for control, while the steering committee makes strategic decisions. A quality manager monitors compliance with standards. If delays occur, everyone immediately knows who is responsible – and solutions are found quickly.
Principle 3: Learning from experience
Experience gained from completed projects is systematically documented and incorporated into new projects. This helps to avoid mistakes and reinforces proven methods.
Practical example
A manufacturing company conducts retrospectives after each project phase. Communication problems in an earlier project led to the introduction of a standardized communication protocol that makes future projects significantly more efficient and reliable.
Guiding principle 4: Management by stages
Projects are divided into clearly defined phases, the completion of which is checked and approved. This ensures that the project remains controllable and manageable.
Practical example
When developing new software, the work is divided into phases such as planning, design, implementation, testing and rollout. After each phase, the following is checked: have the objectives been achieved? Are the risks manageable? If problems arise, the steering committee decides on corrections or adjustments.
Principle 5: Management by exception
Management only intervenes in the event of significant deviations. Within defined tolerances, the project team works independently, thus conserving management resources.
Practical example
A construction project defines tolerances for budget, time and quality. The team resolves overruns of up to 5% itself, and the steering committee is involved for overruns of 15% or more. This allows management to focus on critical decisions.
Basic principle 6: Product orientation
The focus is on clearly defined, high-quality end products – not just on activities. The aim is to deliver specific results that meet requirements.
Practical example
When developing an app, the team defines which functions and quality criteria must be met from the outset. Instead of getting bogged down in tasks, they regularly check whether the product meets the user requirements.
Principle 7: Adapting to the project environment
PRINCE2 is flexibly adapted to the respective project. This makes it equally suitable for small, agile projects and large, complex projects.
Practical example
A start-up uses PRINCE2 in a simplified, agile form with little bureaucracy. A large corporation, on the other hand, uses the complete framework including detailed documentation. Both adapt PRINCE2 to best suit the project – sometimes flexibly, sometimes in a structured way.
The 7 practices of the PRINCE2 method
The seven practices of PRINCE2 form the basis of structured project management. They ensure that all important aspects are considered and managed from the start to the finish of a project. While the principles provide the framework, the practices ensure that it is consistently implemented in practice.
Practice 1: Business case – justification and profitability
The business case justifies why the project is being carried out at all. It shows the expected benefits and is regularly reviewed throughout the entire project. This is how we ensure that costs and benefits continue to be balanced even when conditions change.
Practical example
A company wants to introduce a new ERP system. The business case shows the advantages. If the basic conditions change, it is checked whether adjustments are necessary – for example, to the functional scope or the goals.
Management products which support practice 1
Business case
Benefits management approach
Sustainability management approach
Practice 2: Organization – allocation of roles and stakeholder management
The practice of organization regulates the roles, responsibilities and decision-making processes. A clear structure and good stakeholder management avoid misunderstandings and ensure that everyone involved knows what needs to be done.
Practical example
In an international construction project, clear roles are crucial – from technology to sales. A defined project organization and regular coordination ensure smooth operations.
Management products which support practice 2
Communication management approach
Project management team structure
Role descriptions
Practice 3: Quality – Ensuring and controlling results
Quality means defining clear requirements from the outset and regularly checking whether these are actually being met. This is how products and results are created that meet expectations – both technically and in terms of content.
Practical example
A software company is developing an app. Quality standards are defined at the very beginning. Tests during development ensure that the app works and that users like it.
Management products which support practice 3
Product description
Quality management approach
Quality register
Product register
Practice 4: Plans – Structured planning and milestones
Plans structure the project. They define tasks, dates and milestones. With a good plan, we keep an overview and recognize early on if something is getting out of hand.
Practical example
When introducing a new production line, there is a clear plan for each step – from procurement to training. Delays can be quickly identified and remedied.
Management products which support practice 4
Plan (project, stage, team, exception)
Project product description
Work package description
Practice 5: Risks – Dealing with uncertainties and opportunities
Risks are part of every project. It is important to recognize and manage them at an early stage. PRINCE2 therefore requires systematic risk management that also takes opportunities into account.
Practical example
When setting up a new network, risks such as supply bottlenecks or new requirements are identified early. Contingency plans ensure that the project remains successful nonetheless.
Management products which support practice 5
Risk management approach
Risk register
Practice 6: Changes – Change management during the course of the project
Projects change. The changes practice ensures that new requirements are evaluated and implemented in a structured manner – without losing sight of the overall goal.
Practical example
A customer requests additional security features for a portal. With a clear change process, it is checked whether and how the requests can be integrated – without jeopardizing the project.
Management products which support practice 6
Issue management approach
Issue register
Issue report
Practice 7: Progress – Monitoring and controlling project progress
The practice of progress ensures that the project is always kept in view. Regular status reports, meetings and clear key figures help to identify the current status and to take countermeasures in good time.
Practical example
When a new software is introduced, progress is tracked using dashboards and milestones. If there are delays, immediate action is taken to get the project back on track.
Management products which support practice 7
Digital and data management approach
Daily log
Lessons log
Checkpoint report
Highlight report
Lessons report
Exception report
End stage report
End project report
The 7-phase process of the PRINCE2 method
The successful implementation of a project depends largely on how systematically it is planned,managed and completed. PRINCE2 structures the project process into seven clearly defined processes, each containing specific tasks and decision-making mechanisms. Each process builds on the previous one, ensuring that the project is consistently managed from the initial idea to the final evaluation. The seven processes are explained below and illustrated with practical examples.
Phase 1: Starting up a Project (SU) – first steps and defining objectives
The first process serves to prepare the project before its official start. In this phase, basic information is collected and the goals are defined. The project team is appointed including an executive and a project manager. It determines whether the project is feasible and defines the framework conditions. Here, the project idea is critically scrutinized and an initial assessment of the risks and opportunities is carried out. This project preparation forms the basis for the subsequent detailed planning process. A project description is created.
Phase 2: Initiating a Project (IP) – Detailed Planning and Approval
In the initiation process, the project is comprehensively planned. The project manager creates a project initiation document with the planning of the activities in the project, including the project plan and baseline plans for the performance targets of time, costs, quality, scope, risk and benefits. The project board approves the project plan. The business case is refined and used as a decision-making tool for project approval. The goal of this phase is to create a solid foundation on which the entire project can build.
Phase 3: Directing a Project (DP) – Decision-making by the project board
The “Directing a Project” process focuses on the strategic management of the project. The steering committee, client or main decision-making body start the project, decide on the next phases, respond to escalations, etc. The project board assumes responsibility for overall management. It makes strategic decisions, regularly reviews project progress and ensures that the project meets the defined goals. The board only intervenes in the event of significant deviations and ensures that the necessary resources and support are provided.
Phase 4: Managing a Stage Boundary (SB) – Handover and alignment to new project phases
After a project phase has been completed, the phase transition process takes place. After each phase, the project manager and project board/steering committee review the scheduled progress of the project and its conformity to the requirements. Project managers hold a review meeting with the project team to capture all lessons learned and improve the next phase. The project board decides whether to continue the project. Detailed planning for the following phase is carried out (resource planning, detailed process andtime planning).
Phase 5: Controlling a Stage (CS) – Daily control by the project manager
During a single project phase, the project manager takes over operational control. In this process, daily activities are planned, monitored and, if necessary, adjusted. The project manager puts together work packages and hands them over to team managers or assigns them to teams. The project manager checks progress, coordinates team work and ensures that all activities remain within the defined tolerances. Team managers coordinate the daily work and are the link between the project manager and the project teams. Regular status reports and meetings make it possible to react to problems at an early stage and to meet the planned goals.
Phase 6: Managing a Product Delivery (MP) – Coordination between teams and management
This process focuses on the actual creation and delivery of the defined products. The focus is on close coordination between the various teams involved in the development and management. The aim is to ensure that the developed results meet the defined quality standards and are delivered on time. Continuous coordination and control ensure that the project results correspond to the original business case.
Phase 7: Closing a Project (CP) – Documentation and Lessons Learned
The last process in PRINCE2 is dedicated to the formal completion of a project. Here, all results are finally evaluated, the project team concludes the project and documents the lessons learned. The phase includes a final evaluation in which the entire project process is analyzed. Successes are celebrated, but potential for improvement for future projects is also identified. The systematic documentation of lessons learned helps organizations to continuously learn from past projects.
What roles and responsibilities are there in PRINCE2?
The successful execution of a project is based not only on clearly defined processes and principles, but also on a precise assignment ofroles and responsibilities. PRINCE2 places a strong emphasis on clearly defining each role within a project and assigning specific tasks to them. This ensures that all parties involved know who is responsible for which decisions and how the collaboration between the various stakeholders is organized.
According to PRINCE2®, a project has three primary stakeholder groups:
Executives ensure that a project yields a return on investment.
Users will apply the project products and thus benefit directly from them.
Suppliers provide resources, knowledge and skills and produce the project products.
These three primary stakeholder groups must be represented in the project management team and the project board. This is guaranteed by the following fundamental roles and positions in PRINCE2:
Project board (steering committee)
The project board forms the strategic management level and ensures that the project meets business objectives. It is composed of the most important stakeholders – for example, executives from finance, operations and IT. Its tasks include approving plans, monitoring progress and releasing resources. It makes strategic decisions, intervenes in the event of deviations and maintains business justification.
Senior user / senior supplier
These roles represent the interests of the users and suppliers. The Senior User ensures that the requirements and quality criteria of the end users are met. The Senior Supplier ensures the availability of resources, technical know-how and the quality of implementation. Both work closely together to create a balance between user needs and technical feasibility, and sit together with the client on the project board.
Project Manager
The project manager manages the project operationally and is responsible for the planning, coordination and monitoring of all activities. He ensures that deadlines and budgets are met and is the interface to the project board, to which he reports regularly.
Project assistance and project assurance
The project assistant provides support with project documentation, organization and communication. The project assurance independently monitors compliance with specifications and reports to the project board.
Change authority
The change authority decides on change requests that arise during the project. It checks the effects on costs, time and quality and only approves reasonable adjustments.
Team Manager
The Team Manager leads one or more teams, plans the tasks and monitors the quality of the results. He provides technical support and ensures that objectives are met within the work package.
What's new in PRINCE2 7?
With the publication of PRINCE2 7 in 2023, the framework will be responding to the changing requirements of modern companies. The latest version will build on the proven principles,practices and processes of previous versions, but will integrate current insights and best practices from project management.
Major innovations in PRINCE2 7 include:
| Flexibility and scalability: PRINCE2 7 has been designed to be more adaptable to different project sizes and complexities. Organizations can customize the scope of the methodology without losing structure. | |
| Updated processes and practices: The processes and practices have been modernized to better integrate with digital work environments. This means that the documentation processes are simplified and more digitally supported. | |
| Stronger integration of agile elements: Although PRINCE2 is classically structured, PRINCE2 7 takes into account the increasing importance of agile working methods. It lays the foundation for a hybrid approach in which rigid process steps can be combined with flexible, iterative methods. | |
| Improved communication and collaboration: PRINCE2 7 supports more transparent and effective collaboration within project teams and between stakeholders with new tools and clearly defined communication channels. | |
| Focus on continuous improvement: PRINCE2 7 places even more emphasis on collecting and utilizing lessons learned in order to systematically anchor the continuous improvement process in projects. |
PRINCE2 Agile: Is the PRINCE2 method agile?
In principle, PRINCE2 can be assigned to the classical project management methods. However, in addition to the classical variant, an agile variant of PRINCE2 has now been established: PRINCE2 Agile®. Since 2015, an additional manual has described the integration of agile frameworks into the PRINCE2 process model. Agile methods such as Scrum and Kanban are characterized by their flexibility, rapid iterations and high adaptability. PRINCE2 Agile integrates these elements so that organizations can benefit from both worlds.
What is PRINCE2 Agile? PRINCE2 Agile combines the flexibility and responsiveness of AgilePM with the clearly defined overarching process control framework of PRINCE2. PRINCE2 Agile was developed for companies and individuals who use PRINCE2 and also want to benefit from the advantages of agile methods. The integration of agile approaches primarily relates to the concrete implementation. PRINCE2 Agile thus also enables agile work in complex projects and is a popular method for hybrid project management.
Strengths and advantages of the PRINCE2 method as propagated
PRINCE2 can be applied to projects of any type, size, organization, geography and culture.
PRINCE2 delivers standardized projects that have a consistent approach, vocabulary and documents. Anyone familiar with a method can quickly find their way around a carefully managed PRINCE2 project.
The PRINCE2 guideline is management by exception. This allows project managers to carry out their work without unnecessary interference, and higher-level managers only have to intervene at the points where the project is running outside the tolerance limits.
Templates with the required substructures are available for each document type required by PRINCE2. This results in standardized and complete documentation.
PRINCE2 provides its own product-based planning technique, with integrated requirements analysis. This reduces the likelihood of projects being started under the wrong conditions and subsequently failing.
Presumed weaknesses and disadvantages of the PRINCE2 method
Only PRINCE2-specific techniques are described. However, it may well be necessary for project management staff to develop further knowledge in order to be able to apply commonly used techniques such as critical path analysis or earned value analysis.
Soft skills/leadership qualities as a further important qualification for the project manager are not directly considered in PRINCE2.
Integration of PRINCE2 with other methods and frameworks
PRINCE2 is a powerful framework for managing individual projects. However, projects rarely stand alone. They are often part of larger initiatives, such as programs or portfolios. You will also regularly encounter topics such as risk management or IT-specific requirements in projects. This is precisely where PRINCE2 shows its strength: it can be flexibly combined with other recognized methods and frameworks. This allows you to create an integrated control system that is tailored to your organization and its challenges.
Portfolio and program management with MoP® and MSP®
Many organizations manage not only individual projects, but also a large number of initiatives that contribute to overarching business objectives. PRINCE2 focuses on managing the individual project – MoP® (Management of Portfolios) and MSP® (Managing Successful Programmes) are available to help manage entire project landscapes.
MoP helps you select the right projects and allocate resources effectively. It ensures that your organization implements precisely those projects that bring the greatest benefit. PRINCE2 comes into play when it comes to the actual implementation of these projects.
MSP, on the other hand, is aimed at managing programs, i.e. several interrelated projects that together implement a strategic change. PRINCE2 projects can be managed as building blocks of a larger program. By combining PRINCE2 and MSP, you create a clear framework: MSP sets the direction, PRINCE2 provides the methodology for implementation.
Risk management with M_o_R®
Risk management is part of every successful project. Although PRINCE2 has its own risk management guidelines, a deeper, more specific approach is necessary, which is where M_o_R® (Management of Risk) PRINCE2 ideally complements.
M_o_R provides a systematic framework for identifying, evaluating and managing risks in projects, programs and the entire company. While PRINCE2 keeps an eye on the risks of a project, M_o_R provides additional strategies and procedures to treat risks consistently across the company. This combination ensures consistency and security, especially for companies with many parallel projects.
IT project management and PRINCE2 in software development
Many companies also use PRINCE2 in IT and software projects. In these projects, questions often arise as to how classic project management structures can be combined with agile methods such as Scrum® or SAFe.
PRINCE2 offers PRINCE2 Agile®, a specially extended variant that combines agile working methods with the proven PRINCE2 structures. This allows you to benefit from the advantages of both worlds: the flexibility of agile development teams is maintained, while PRINCE2 provides the necessary control and transparency.
In software development, you can also combine PRINCE2 with ITIL® or DevOps. ITIL manages your service processes, while PRINCE2 ensures the structured implementation of software projects. DevOps builds the bridge to continuous integration and delivery of software (CI/CD), with PRINCE2 ensuring overarching project management and release processes.

Thilo Menges, Head of Corporate Development, Medical University of Lausitz - Carl Thiem
“About 20 project managers, who are responsible for projects in the three core areas of IT, digitization & innovation and research, are actively involved in using BCS, since they partly draw on the same resources to carry out their projects. For our major projects, we use the PRINCE2 project management method, which optimally supports BCS with functionalities and corresponding assistants, as far as it suits the organization in each individual case.”
Apply the PRINCE2 method: certifications and training
Anyone who wants to apply PRINCE2 successfully in projects will benefit from sound training. PRINCE2 certifications provide you with exactly this foundation. They not only prove your knowledge, but also give you a structured understanding of how to apply PRINCE2 in practice. The certifications are divided into two levels: Foundation and Practitioner.
PRINCE2 Foundation certification is aimed at those new to project management or those who want to understand the basic principles and terminology of PRINCE2. You will learn how the framework is structured, which processes and roles are available and how PRINCE2 works in a structured way. With Foundation certification, you demonstrate that you understand the method and can work in projects with PRINCE2 teams. The route to Foundation certification usually involves official training, which often lasts two to three days. At the end, you take an exam that tests your knowledge of the basics.
The PRINCE2 Practitioner certification builds on the Foundation. It is aimed at people who want to actively apply and manage PRINCE2 in projects. The aim of the Practitioner level is to use PRINCE2 flexibly and in a way that suits the situation. Here you will learn how to adapt the method to different projects, how to evaluate specific project situations and which decisions are necessary in which step. For Practitioner certification, you will usually attend an advanced training course (usually two days) that focuses on practical application. The subsequent exam is complex: in a scenario-based test, you will have to apply your knowledge in practice and show how you would deal with typical project situations.
Both exams are conducted by PeopleCert, the official PRINCE2 examining body. There are numerous PRINCE2 training providers, ranging from large training companies to specialized PRINCE2 training providers. It is important that the training is accredited and adheres to the official syllabus. To prepare successfully, it is recommended that you work through the official PRINCE2 manual intensively.
Which project management software is suitable for the PRINCE2 method?
If you are looking for a project management software that can map the PRINCE2 method in the best possible way, without you having to make concessions or even do without certain PRINCE2-specific functions, you should already pay attention to the corresponding functions when selecting the software. As our current market overview and project management software comparison show, not every popular and well-known project management software is suitable for implementing projects according to PRINCE2. Follow our 9-step plan when selecting project management software to evaluate purposefully and make the right decision in the long term.
Projektron BCS not only fully supports project management using the PRINCE2 method, but also provides a suitable assistant that supports you from the very beginning when planning your projects using PRINCE2 and reliably accompanies you through to the completion of a project. The PRINCE2 functions in Projektron BCS include, among other things:
A quality register in which you define criteria for your project success.
Tolerance limits that you can store for your project values together with the steering committee.
Comprehensive planning tools for rough and detailed planning of your project phases.
Specific resource management with resource preview.
Change management for open points that the steering committee can check and accept with a single click.
Report generator, for example for your business case.
Easy assignment of project roles and display as an organizational chart.
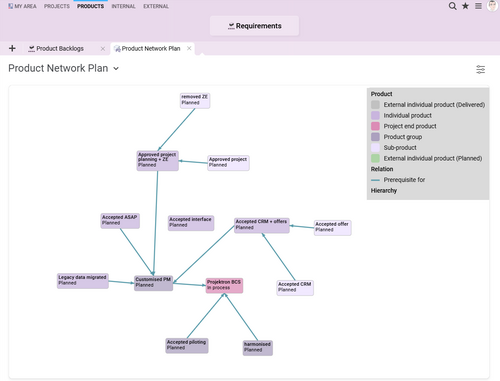
Graphical network plan for related products with predecessor-successor relationships.
Discover Projektron BCS as PRINCE2 software and test BCS right now with no obligation!
Best Practice: PRINCE2 implementation at DVZ M-V with Projektron BCS
DVZ Datenverarbeitungszentrum Mecklenburg-Vorpommern GmbH, the state's central IT service provider, has been working with the process-oriented project management method PRINCE2 since 2008. Every year, around 100 development projects and over 1,000 operational and service projects with budgets between €10,000 and €5 million are implemented. In software projects, PRINCE2 is combined with Scrum. With 17 years of experience, over 100 qualified employees and 25 PRINCE2 practitioner certifications, DVZ has a high level of maturity. A dedicated project management office (PMO) monitors quality and supports project managers.
In 2016, the company was looking for software that fully supports PRINCE2 and reduces the high level of manual work involved in day-to-day project work in order to meet the increasing demands on modern and efficient project management. In Projektron BCS, DVZ found a solution that perfectly meets its methodological and organizational requirements.

Arne Hennes, Head of the Project Management Office (PMO) at DVZ GmbH
“With Projektron BCS, we have found a software that allows us to implement PRINCE2 consistently, efficiently and in a user-friendly way. In particular, the integration of assistants, workflows and reports makes our work much easier and more structured.”
BCS itself was introduced as a PRINCE2 project. To promote acceptance within the company, a multi-level training concept was developed and an internal coaching program was established that is still in place today. Supplemented by an internal trade fair, employees were able to familiarize themselves with the new solution at an early stage.
DVZ placed particular emphasis on the complete mapping of the PRINCE2 project process: with the BCS-supported assistants, the project managers are guided securely through all the phases – from initiation to completion. A graphical product structure plan always shows the current project status transparently, while standardized reports and dashboards support communication with management and the steering committees.
By introducing Projektron BCS, the number of tools used was reduced from 15 to a single solution. Manual and paper-based processes that were previously necessary are now completely eliminated. The PMO also benefits from a significant reduction in administrative effort and better control of the entire project landscape.
An additional added value: data from other systems such as SAP or the service recording can be synchronized via interfaces. This means that decision-relevant information is available in real time – a basis for successful project management and control according to PRINCE2.
In the success story, Arne Hennes provides detailed insights into the use of Projektron BCS for implementing project management according to PRINCE2 at DVZ GmbH.
Conclusion: Why PRINCE2 remains relevant for companies
PRINCE2 is one of the world's most recognized project management standards for good reason. The method offers companies a clearly structured approach that can be flexibly adapted to different types of projects and company sizes. PRINCE2 remains relevant, especially in times of complex and interdisciplinary projects, because it clearly clarifies responsibilities, facilitates control through defined processes and ensures economic justification of the project from the outset.
Companies benefit from PRINCE2 because the method not only provides support during project planning, but also ensures transparency during the implementation and control of a project. By focusing on the results and benefits for the company, project teams and decision-makers always keep the most important goals in mind.
In addition, PRINCE2 helps to clearly define roles and tasks. Especially in large projects with multiple participants, this ensures that everyone knows what is expected of them. For companies that regularly carry out projects, PRINCE2 creates a common language and clear processes – an important basis for efficiency and quality.
The future of PRINCE2 and possible developments
Even though PRINCE2 is already an established framework, the method continues to develop. In recent years, topics such as agile project management, hybrid approaches and digital transformation have significantly changed project management. PRINCE2 is responding to this and increasingly integrating flexible and agile elements to make projects more dynamic and adaptable.
Future developments could be geared even more towards combining classic and agile methods. This could lead to an upcoming version of PRINCE2 providing even more targeted guidance for hybrid project environments – i.e. for projects that require both clear planning phases and agile, incremental development steps.
Another important topic is the integration of PRINCE2 into modern IT and software projects, where speed and adaptability are crucial. Here, too, PRINCE2 is already showing strengths with its product-based approach, but it is likely to address these requirements even more closely.
Tips for implementing PRINCE2
If you want to use PRINCE2 in your company, it is advisable to consider a few points:
Start by analyzing your existing project management processes. This will help you to see how PRINCE2 can support your company and where adjustments are needed.
Don't just train individuals, train entire project teams. This will ensure that everyone involved is familiar with PRINCE2 and that the method is actually used in their day-to-day work.
Use PRINCE2 flexibly and adapt it to your company size and culture. Not every project needs the complete set of processes – it's important to choose the right elements.
Combine PRINCE2 with other methods if it makes sense for your projects. A hybrid approach of PRINCE2 and agile methods such as Scrum or Kanban can be very effective, especially in agile or innovation-driven projects.
Start with small projects to gain initial experience with PRINCE2 before managing larger projects entirely according to the method.
Emphasize the importance of regular reviews and lessons learned. This will help you to continuously improve your project processes and adapt PRINCE2 even better to your company.
Use the management templates and checklists provided by PRINCE2. These help you to ensure that no important points are overlooked and create a standardized approach for all projects.

Über den Autor
The employees in our user support team know the functions and modules of Projektron BCS like the back of their hand. They also know the needs and requirements of each individual customer with regard to project management software. With the experience of over 1,000 successful product launches, they are experts at understanding customer requirements and translating customer-specific workflows into the functionality of Projektron BCS.
More interesting articles on the Projektron blog

Hybrid PM
Classic or agile? If the decision between these two approaches is difficult, a combination of two or more project management methods is probably the right way to go. Find out everything you need to know about hybrid project management in this article.

Scrum in software development
When it comes to agile software development methods, there is one term you cannot avoid: Scrum. But what exactly is Scrum and how does it develop its strengths in software development?

Project management software comparison
Get an up-to-date overview: We compare 15 of the most popular and best project management software solutions. Start here, discover the market and compare for yourself!

Process modeling with BPMN
BPMN - the standard for process modeling. BPMN stands for Business Process Model and Notation and is an international modeling language for business processes. You can find out everything about BPMN and how you can use it here.
FAQ – PRINCE2
What does PRINCE2 mean?
PRINCE2 stands for “Projects in Controlled Environments.” The idea behind the method is to make projects structured and easy to follow. It makes sure that every step is planned, monitored, and controlled. It's also based on tried-and-true processes and best practices from real life. This gives you the assurance that your projects are well prepared and reliably implemented.
What is PRINCE2 and what is PRINCE2 Agile?
PRINCE2 is a classic project management method that is characterized above all by its process orientation and clear roles. PRINCE2 Agile combines this structure with agile working methods such as Scrum or Kanban. This gives you the proven planning and control of PRINCE2, complemented by greater flexibility and rapid adaptability. This combination is particularly well suited to dynamic projects where you need to react regularly. It allows you to get the best of both worlds.
How does PRINCE2 work?
PRINCE2 is process-oriented and structures your projects into clearly defined phases. At the beginning, you define the project goals and their benefits, and then divide the work into manageable stages. Each phase is planned, executed, and reviewed before the next one begins. In addition, there are clear roles and responsibilities for everyone involved, so that everyone knows exactly what to do. Regular reports allow you to stay in control of progress, costs, and risks at all times.
Why should you use PRINCE2?
PRINCE2 offers you a proven, easily adaptable project management method with a clear and structured approach. It enables you to plan projects better and identify risks at an early stage. It also uses standardised terms and processes, which makes collaboration easier. The method is internationally recognised, which also benefits you in terms of certification and career development. Overall, PRINCE2 helps you make your projects more transparent, efficient, and successful.
When is PRINCE2 project management used?
You use PRINCE2 when you want to manage projects in a structured way with clear processes. It is particularly well suited for larger or more complex projects with many participants and high demands on structure, quality, and control. PRINCE2 is also useful if you regularly need status reports and decision-making criteria. It can also be easily adapted to the size and type of your project. This makes the method versatile and applicable in many industries.
How difficult is PRINCE2?
PRINCE2 is easy to understand if you take it step by step. The method is very well structured and comprehensively documented in a manual. To obtain Foundation certification, it is sufficient to learn the basics and the process descriptions. It becomes more challenging at the Practitioner level, as you then have to apply the method in a practical context. With the right preparation and some project experience, this is also easily achievable.
What can be adapted after PRINCE2?
PRINCE2 is designed so that you can adapt it flexibly to your project size, type, and industry. You decide which processes, roles, and documents you want to use in full or in part. The level of detail in the planning and the reporting cycles can also be customized. This scalability helps you avoid the method becoming overly bureaucratic. This ensures that PRINCE2 fits your needs exactly.
What is defined when adapting PRINCE2 to the project?
During adaptation, you determine which PRINCE2 processes you will use and how intensively they will be implemented. You also define the roles and responsibilities appropriate to your organization. The content and format of the project documents are also adapted to the size of your project. You also define how you will monitor progress and risks. This makes PRINCE2 a tailor-made tool for your project.
What is PRINCE2 certification?
PRINCE2 certification is official proof that you know the method and can apply it in projects. There are two levels, “Foundation” and “Practitioner,” which test your knowledge and practical skills at different levels of intensity. Passing the exam improves your job prospects and helps you take on responsibility in projects more quickly. In addition, the certification is internationally recognized and regularly updated. This ensures that you remain up to date with the latest project management best practices in the long term.
What are the benefits of PRINCE2 certification?
With PRINCE2 certification, you demonstrate that you have mastered the fundamentals and methods of project management according to this international standard. You improve your career opportunities and professional competence in the eyes of employers and clients. The certification also helps you manage projects in a more structured and efficient manner. For many companies, it is also proof that you can professionally support their project processes. This gives you a clear advantage in the job market.
What advantages does PRINCE2 offer compared to other project management methods?
PRINCE2 scores with a clear process model that you can easily tailor to different projects. The methodology is recognized worldwide and therefore offers you international application possibilities. In addition, there is a strong focus on cost-effectiveness and ongoing monitoring of project results. Unlike purely agile methods, PRINCE2 provides you with a stable framework while still leaving enough room for adjustments. This makes the method particularly versatile and practical.
How is PRINCE2 applied in practice?
You apply PRINCE2 step by step by going through the seven processes of the method one after the other. You plan each project in a targeted manner, carry it out in controlled phases, and regularly check progress and quality. The clear roles and defined reporting structure help you improve communication and decision-making. PRINCE2 also supports you in risk management and the efficient use of your resources. This allows you to maintain control at all times and ensure that project goals are reliably achieved.